Measurement of Small Photon Numbers in Circuit QED Resonators
1166 浏览Off-resonant interaction of fluctuating photons in a resonator with a qubit increases the qubit dephasing rate. We use this effect to measure a small average number of intracavity photons that are coherently or thermally driven. For spectral resolution, we do this by subjecting the qubit to a Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill sequence and record the qubit dephasing rate for various periods between qubit π pulses. The recorded data is then analyzed with formulas for the photon-induced dephasing rate derived for the non-Gaussian noise regime with an arbitrary ratio of the resonator dispersive shift to decay rate. We show that the presented Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill dephasing rate formulas agree well with experimental results and demonstrate measurement of thermal and coherent photon populations at the level of a few 10−4.
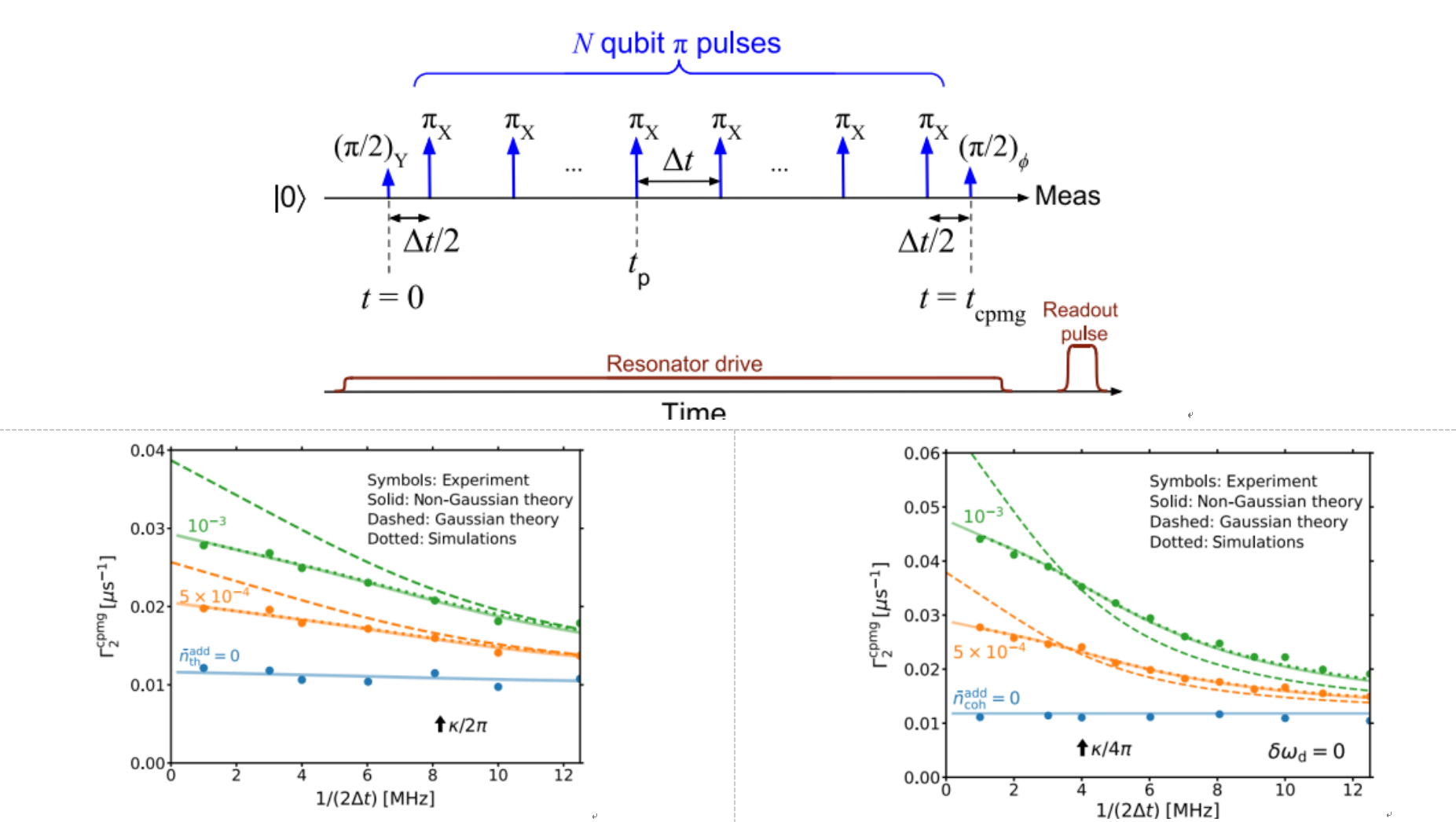
We have derived and validated formulas for the CPMG dephasing rate of a qubit due to thermal and coherent photons inside a resonator. These formulas are valid for an arbitrary ratio 2χ=κ, accounting for nonGaussian noise. We have also demonstrated that these formulas and CPMG data can be used to measure average thermal and coherent intracavity photon populations at the level of ∼10−4 photons. This level of accuracy is probably limited by fluctuations of the qubit T1 and other parameters.
Reference:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.203601
