A linear response framework for quantum simulation of bosonic and fermionic correlation functions
1128 浏览Efekan Kökcü, Heba A. Labib, J. K. Freericks & A. F. Kemper
Response functions are a fundamental aspect of physics; they represent the link between experimental observations and the underlying quantum manybody state. However, this link is often under-appreciated, as the Lehmann formalism for obtaining response functions in linear response has no direct link to experiment. Within the context of quantum computing, and via a linear response framework, we restore this link by making the experiment an inextricable part of the quantum simulation. This method can be frequency- and momentum-selective, avoids limitations on operators that can be directly measured, and can be more efficient than competing methods. As prototypical examples of response functions, we demonstrate that both bosonic and fermionic Green’s functions can be obtained, and apply these ideas to the study of a charge-density-wave material on the ibm_auckland superconducting quantum computer. The linear response method provides a robust framework for using quantum computers to study systems in physics and chemistry.
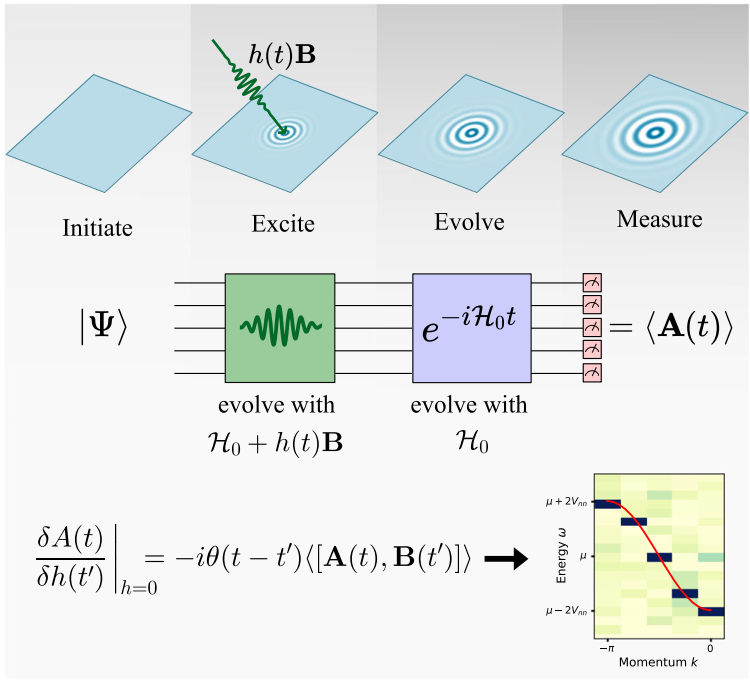
Fig. 1 Linear response method. We establish an equivalence between the experimental measurement of a response function and an ancilla-free quantum simulation under a time dependent Hamiltonian that includes the perturbative excitation h(t)B. Following excitation, the system is evolved under H0, and A is measured. The functional derivative of A(t) = 〈A(t)〉 with respect to h(t’) yields the retarded response function shown in the figure.
Reference: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-47729-z
