Integrated Photonic Quantum Computing: From Silicon to Lithium Niobate
2026-01-30 10:50
40 浏览
Quantum technologies have surpassed classical systems by leveraging the unique properties of superposition and entanglement in photons and matter.
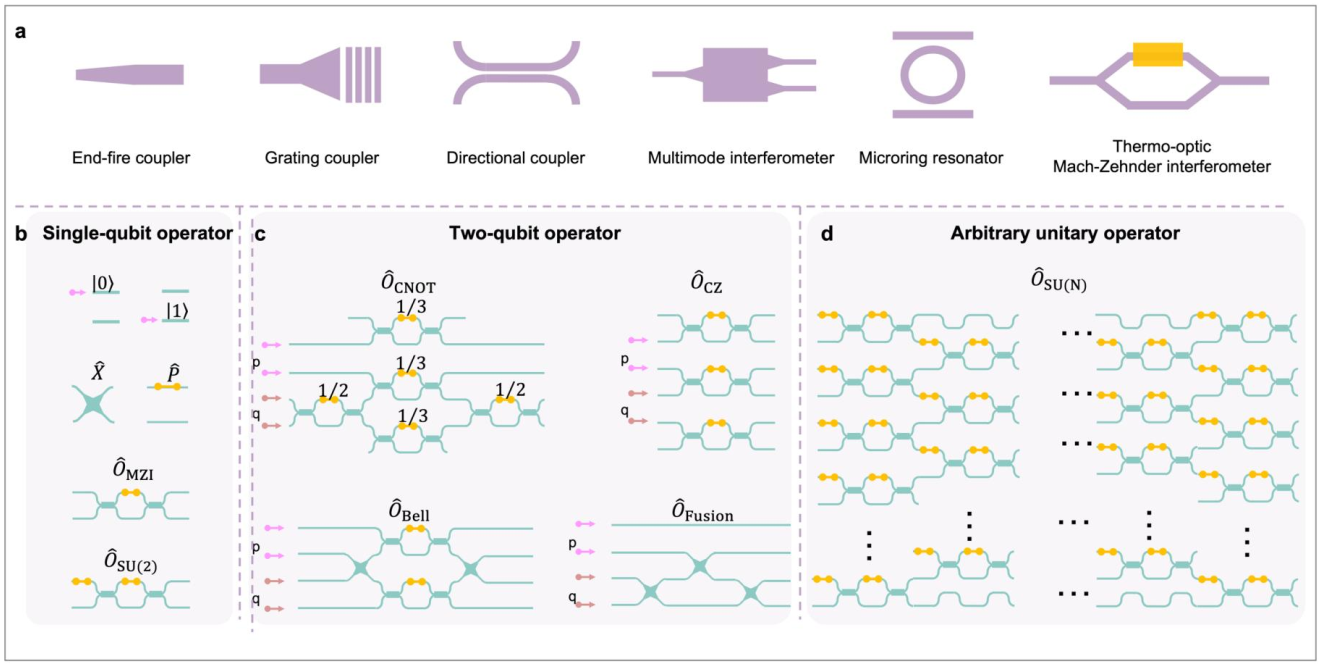
Recent advancements in integrated quantum photonics, especially in silicon-based and lithium niobate platforms, are pushing the technology toward greater
scalability and functionality. Silicon circuits have progressed from centimeter-scale, dual-photon systems to millimeter-scale, high-density devices that
integrate thousands of components, enabling sophisticated programmable manipulation of multi-photon states. Meanwhile, lithium niobate, thanks to its
wide optical transmission window, outstanding nonlinear and electro-optic coefficients, and chemical stability, has emerged as an optimal substrate for fully
integrated photonic quantum chips. Devices made from this material exhibit high efficiency in in generating, manipulating, converting, storing, and detecting
photon states, thereby establishing a basis for deterministic multi-photon generation and single-photon quantum interactions, as well as comprehensive
frequency-state control. This review explores the development of integrated photonic quantum technologies based on both silicon and lithium niobate,
highlighting invaluable insights gained from silicon-based systems that can assist the scaling of lithium niobate technologies. It examines the functional
integration mechanisms of lithium niobate in electro-optic tuning and nonlinear energy conversion, showcasing its transformative impact throughout the
photonic quantum computing process. Looking ahead, we speculate on the developmental pathways for lithium niobate platforms and their potential to
revolutionize areas such as quantum communication, complex system simulation, quantum sampling, and optical quantum computing paradigms.
Link to the article is here.

