Comprehensive characterization of three-qubit Grover search algorithm on IBM’s 127-qubit superconducting quantum computers
2024-06-23 10:12
1058 浏览
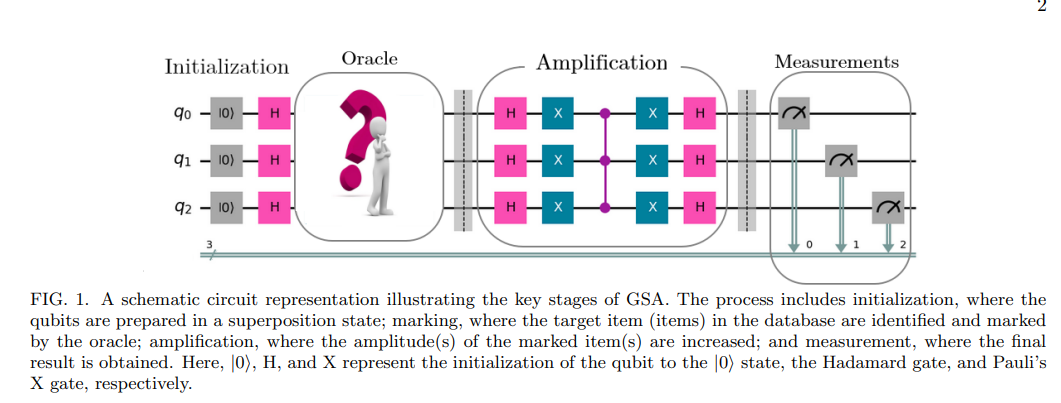
The Grover search algorithm is a pivotal advancement in quantum computing, promising a remarkable speedup over classical algorithms in searching unstructured large databases. Here, we
report results for the implementation and characterization of a three-qubit Grover search algorithm
using the state-of-the-art scalable quantum computing technology of superconducting quantum architectures. To delve into the algorithm’s scalability and performance metrics, our investigation
spans the execution of the algorithm across all eight conceivable single-result oracles, alongside nine
two-result oracles, employing IBM Quantum’s 127-qubit quantum computers. Moreover, we conduct
five quantum state tomography experiments to precisely gauge the behavior and efficiency of our
implemented algorithm under diverse conditions – ranging from noisy, noise-free environments to the
complexities of real-world quantum hardware. By connecting theoretical concepts with real-world
experiments, this study not only shed light on the potential of NISQ (Noisy Intermediate-Scale
Quantum) computers in facilitating large-scale database searches but also offer valuable insights
into the practical application of the Grover search algorithm in real-world quantum computing
applications.

Article: https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.16018
